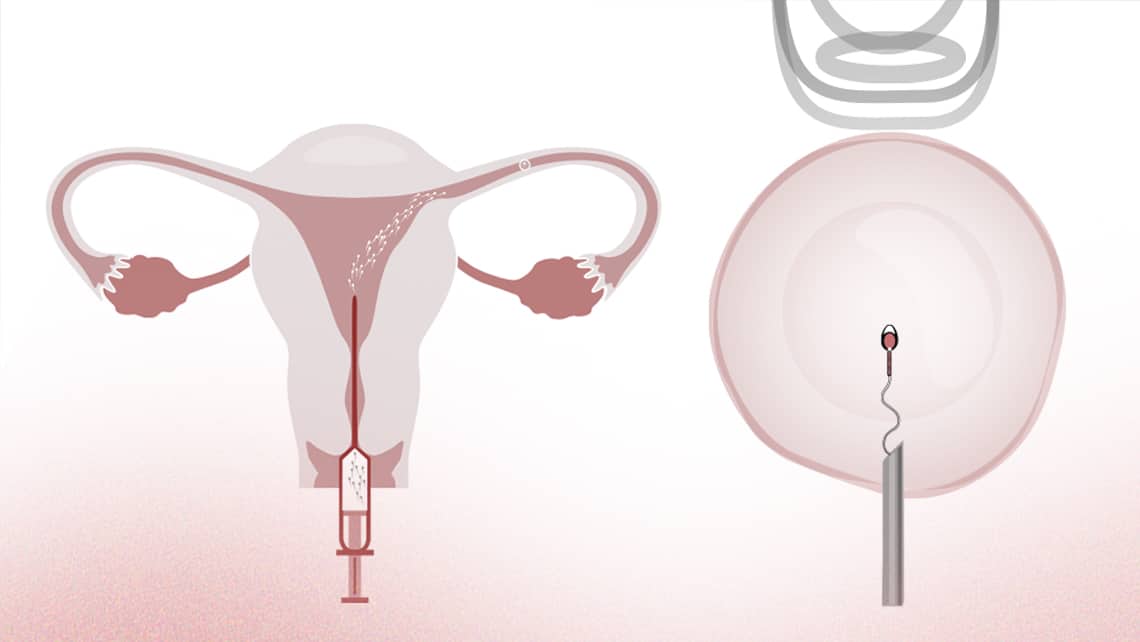
Differences between Artificial Insemination and In Vitro Fertilisation
Artificial insemination is a simple technique carried out on couples with specific fertility problems.
The ideal candidate would be a young woman with permeable fallopian tubes, less than 3 years of sterility and a male partner with normal semen. Artificial insemination is useful for couples that meet these requirements. No more than 4 tries are carried out, and the overall pregnancy rates are 25% – 30 %.
In Vitro Fertilisation is a completely different technique, in which the gametes are fertilised in the reproduction laboratory. This technique has a much higher pregnancy rate and provides more information to the clinic and couple, since the behaviour of these embryos can be observed over several days in the laboratory.
Each technique has its indications. It is very important to diagnose each couple correctly and recommend the most suitable treatment.
The main differences between these two treatments are explained simply below:
| ARTIFICIAL INSEMINATION | IN VITRO FERTILISATION | |
| 1. | This technique introduces previously selected semen into the woman’s uterus that has been prepared by stimulating ovulation. | This technique consists of retrieving a woman’s eggs to be fertilised in the laboratory and later introducing the obtained embryos inside the uterus. |
| 2. | The fertilisation (uniting of the egg and sperm) happens “live” inside the woman, specifically in the fallopian tube. | The fertilisation happens “live” outside the woman, in the laboratory. |
| 3. | It is a simpler technique since it does not require retrieving eggs. | It is a more complex technique since it requires a surgical procedure to obtain the eggs and be fertilised in the laboratory. |
| 4. | The ovarian stimulation should be minimal to avoid the risk of multiple pregnancies. The growth of more than 2 or 3 follicles should make us consider cancelling treatment. | The ovarian stimulation aims to obtain an adequate number of eggs, which ranges between 6 and 15. |
| 5. | It is more affordable if you consider the cost per treatment. | The financial burden is higher, although it is more affordable if you consider the cost per live birth. |
| 6. | The chances of success are lower: about 15% per attempt, considering couples with a good prognosis. | It is the treatment with the highest success rates per attempt. In certain cases, the chances of achieving pregnancy are up to 60%. |
| 7. | Provides no real chance of success in cases of fallopian tube blockage or severe male factor. | The possibilities of success, except in extreme cases, are not necessarily affected by fallopian tube blockage or severe male factor. |
| 8. | It offers very poor results when the sterility time is over 3 years, it is due to a moderate male factor or the woman has endometriosis. | This could be the first option for couples with a prolonged sterility time, moderate male factors or women with endometriosis. |
| 9. | It offers limited information during treatment. | Valuable information is obtained during treatment since important factors are evaluated such as the ovarian response to stimulation, egg quality, fertilisation and embryo development. |
| 10. | This is a good option for couples with a good prognosis (young couples that have not been trying to conceive for a long time without significant semen alterations, fallopian tube blockage or endometriosis). | It is the treatment with the highest chances of success in assisted reproduction and is the first choice in many cases. |
For further information, consult our website: www.institutobernabeu.com/en/
