In Vitro Fertilisation (IVF)
In vitro fertilization (IVF), the main treatment for infertility, allows for higher rates of pregnancy than natural conception.
What is in vitro fertilization?
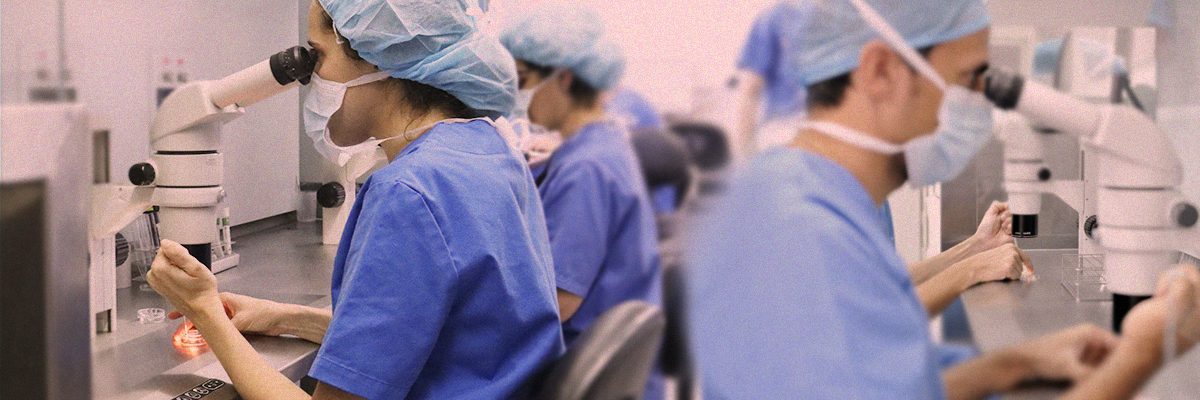
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) is a technique whereby egg fertilization takes place outside the woman’s body. Embryos are created in the laboratory and then placed in the woman’s uterus to stimulate development and achieve pregnancy. This process involves several steps which need to be adequately coordinated. Designing made-to-measure treatment for the patient’s needs, team quality and the clinic’s technology are key to success.
In vitro fertilisation techniques

IVF using the patient’s own gametes
Best treatments and care so that together we can achieve your goal to become parents.
IVF Process

1 day

Patient´s study and preparation
Every patient is a unique individual; for this reason, our treatments at Instituto Bernabeu are tailored for each of our patients. Our aim is to locate the couple’s source of infertility and design the most effective treatment. The male’s sperm and hormone levels are analysed and, if necessary, a urological assessment is performed.
In the case of women, their cervical canal and endometrial cavity are examined, as well as possible alterations in their fallopian tubes and their menstrual cycle patterns. These are accompanied by detailed assessments of the couple’s sexual health.
This process ensures that IVF is the correct solution to the patients’ infertility problems and that they are physically and psychologically ready to begin the cycle. If this is not the case, the patients are offered other treatment options.

~ 8/12 days
Ovarian stimulation
In order to maximise the possibility of pregnancy, we need to obtain more than one oocyte, which is the number a woman’s ovary normally produces.
In order to stimulate production of several oocytes and guarantee their quality, we administer a combination of pharmaceutical drugs. Response is monitored using vaginal ultrasound scans and timely blood analyses: ovulation induction.
The whole process lasts approximately between 8 and 12 days, depending on each case. The treatment can be cancelled if a low or exaggerated ovarian response is observed.

1 day
Egg retrieval
Once the oocytes are mature, we retrieve them with the guidance of a vaginal ultrasound under local anaesthesia and light sedation so that is a completely painless experience. This process only takes 15 minutes and does not require surgery, hospitalisation, stitches or general anaesthesia.
Sperm capacitation
At the same time, the semen is activated to improve its fertilisation potential.

Laboratory fertilisation
The retrieved eggs are taken into the IVF laboratory where they are prepared for insemination.
Oocytes and spermatozoids are placed together for several hours within an incubator which provides the ideal conditions for fertilisation to take place and the subsequent development of pre-embryos. The number of fertilised eggs will not be known until the next day
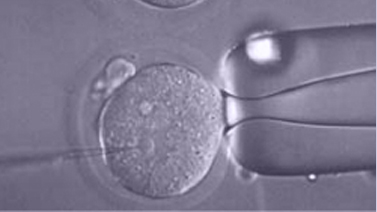
ICSI (Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection)
ICSI is performed on oocytes when the reproduction biologist in charge deems it necessary or when it has been previously agreed upon.
The Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI), consists in the introduction of a single spermatozoid inside a mature egg to achieved fecundation.
ICSI proved to be a revolution in assisted reproduction techniques, as it overcomes most male infertility problems. This technique is used in fertilization when sperm suffers from low count, an abnormal morphology, poor motility or when the sperm is unable to fertilize through IVF. It can also be used with patients suffering from a blocked sperm duct. In this case, a puncture is made in order to extract sperm directly from the testicles.
This procedure is performed using a microscope. Micromanipulation equipment is also used, allowing us to stabilize the egg softly and subsequently place the sperm inside it. Sperm selection is essentially guided by morphological features, although other methods (MACS, IMSI, PICSI) can also be used. More information.

3/5 days
Embryos culture
Fertilisation is followed by development in a culture medium that provides everything that is needed for growth. The embryos are assessed during development.
Growth is periodically assessed because not all human embryos reach blastocyst stage.
It is important to keep in mind that not all of them will fertilise and become viable embryos. There will be good and poor quality embryos and others that will simply block.

1 day
Embryo transfer
Once the blastocyst stage has been reached, embryo transfer takes place. This is an essential step during treatment.
The embryo is places in the mother’s uterus. It is performed with the assistance of an abdominal ultrasound. The culture medium containing the embryo is places inside the uterus. This is a painless and brief process.
Embryos that have not been transferred and wish to be preserved, after vitrification, proceed to storage. After identification, they are deposited in an exclusive location in the cryogenic tanks of our laboratories. For complete security, this location is not shared with other samples, nor with other patients, to protect them from potential cross-infection or inaccuracies.

10/12 days
later

Testing for positive pregnancy
13/14 days after the progesterone medication began, a blood sample is taken from the patient in order to determine whether she is pregnant or not. It consists of detecting beta-hCG levels in blood as this hormone is produced by the embryo and passed on to the mother. It is the first measurable sign sent by the embryo.
If the patient is not pregnant, the medical team involved in the course of treatment assesses the causes and decides what steps need to be taken. The patient is given an appointment in order to be able to tell her about the team’s evaluation of the situation.

15 days later
Pregnancy ultrasound
If the result of the pregnancy test is positive, the patient has an ultrasound scan around two weeks later. Performing this scan any earlier would lead to confusion and doubts since the results are generally not conclusive at this stage.
IVF is a highly flexible procedure. It is possible to use the patient’s own eggs or the donor’s. Likewise, it is possible to use the partner’s sperm or the donor’s. This technique has made gestation possible for women without a partner or for same sex couples (ROPA). Furthermore, IVF allows for preimplantation genetic diagnosis and thus, drastically reduces the risk of having children with genetic disorders.
Indications for in vitro fertilization
- Failure of previous insemination attempts
- Age-related infertility
- Recurrent miscarriages
- Ovarian failure
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Endometriosis
- Low count or motility of spermatozoa, or altered percentage of their abnormal forms
- Obstruction or ligation of the fallopian tubes
- Single motherhood by choice
- Lesbian, bisexual or transgender motherhood
- History of genetic diseases
- Vasectomy
- Infertility of unknown origin
Benefits of IVF
In vitro fertilization is the most common treatment in reproductive medicine. It means oocytes are fertilised by sperm outside the woman’s body. Embryos are then transferred in order to favour implantation.
- IVF is a versatile procedure. Oocytes used may come from the patient or from a donor. The sperm may come from the patient’s partner or from a donor.
- The technique has made it possible for single women or women in a same-sex relationship to get pregnant (ROPA).
- It makes it possible to perform pre-implantation genetic diagnosis, a procedure that reduces the risk of giving birth to children with genetic disorders.
- Success rates are high. (see: statistics in Instituto Bernabeu)
Technology and specific treatment units
Our own cutting-edge technology and specialised professional for every therapeutic need:
Secondary effects and disadvantages of IVF
Usually, patients can resume their activity the day after egg retrieval or transfer. Rare side effects include slight bloating, increased breast tenderness, cramping or constipation.
In terms of disadvantages, it should be pointed out that there is a low risk of complications. These include ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome and multiple pregnancies. Learn more about possible IVF complications.
Requirements for IVF
A study of the couple is performed where the male seminal quality is evaluated. The female partner must also generate eggs and be free of uterine malformations.
At Instituto Bernabeu, the fertility study is personalised in order to tailor treatment for each patient and thus, optimise the results. Find out more about our:
- Fertility study that is already started in
- The first fertility appointment

Post-cycle delayed transfer of frozen embryos:
Usually, the transfer of embryos resulting from the in vitro fertilization process was carried out in the same stimulation cycle after embryo development. However, it has been proven that in many cases this is not the most convenient for gestational nesting: the development of several follicles in the ovaries when receiving different stimulation, as well as hormonal medication, can de-structure the endometrium and disturb its implantation capability.
Therefore, in certain patients it may be indicated to freeze the embryos and postpone their transfer to a subsequent cycle (cryotransfer) once the endometrium has recovered. This strategy is increasingly used, and not only in patients with implantation failure, which is a primary indication.
FROZEN EMBRYO TRANSFER IN NATURAL CYCLE:
The transfer can be carried out in a natural cycle by coinciding the cryotransfer after ovulation – as long as the patient has regular menstrual cycles, as her ovary will be able to prepare her endometrium in a natural way just as her uterus is prepared each month for a theoretical implantation of the embryo. Learn more.
TRANSFER OF FROZEN EMBRYOS IN SUBSTITUTED CYCLE:
The substituted or “artificial” cycle consists of performing the cryotransfer once endometrial receptivity has been optimized with the administration of estrogens and progesterone. It is indicated in anovulatory patients, with irregular cycles or without ovarian function. Although it may also be advisable in certain norm ovulatory patients. Learn more.
IVF success statistics at Instituto Bernabeu
Statistics refer to overall data and should not be extrapolated to any one particular case. It is important to keep in mind that it is essential to always establish a personalised prognosis. The data reflects statistics without PGS (CCS) and elective vitrification.
The cumulative pregnancy rate is indicated below (it refers to pregnancies achieved following the egg retrieval/collection procedure. This includes transfer of fresh embryos and a possible transfer of cryopreserved embryos when the objective is not achieved in the first transfer).
SUCCESS RATE STATISTICS FOR IN VITRO FERTILISATION (IVF) AT INSTITUTO BERNABEU 2023
Patient age | Success rate |
|
Positive pregnancy test <35 years of age | 51,5% |
|
Cumulative positive pregnancy test <35 years of age (1 fresh transfer plus 2 cryotransfers, with no PGD and elective vitrification) | 89,3% |
|
| Positive pregnancy test 35-39 years of age | 48% |
|
| Cumulative positive pregnancy test 35-39 years of age (1 fresh transfer plus 2 cryotransfers) | 88,7% |
|
Positive pregnancy test ≥40 years of age | 33,3% |
|
Cumulative positive pregnancy test ≥40 years of age (1 fresh transfer plus 2 cryotransfers) | 64,7% |
|
Embryo quality | Success rate |
|
| Global % of embryos that reach the blastocyst stage | 66,3% |
|
| Transfer performed during blastocyst stage (day 5) | 86,3% |
|
Overall % of cycles in which embryos are frozen (All age ranges are included in courses of treatment with no pgd and elective vitrification) | 67,8% |
|
SOFT-FIV
Soft-IVF stands as an alternative to conventional ovarian stimulation. Its goal is to limit the number of eggs to be retrieved and therefore alleviate the treatment’s burden for patients without compromising the accumulated options to fall pregnant. SOFT-IVF does not require as much medication and, unlike traditional medication, not all is injected. The main difference with traditional IVF lies in the ovarian stimulation stage as the procedures that follow are similar.
The main advantages are:
- Lower medication dose.
- Fewer required visits to the clinic.
- Less discomfort and side effects linked to ovarian stimulation as it is gentler.
It is indicated for:
- Women under 35 years of age with good ovarian reserve and good prognosis.
- Previous exaggerated ovarian response that should be avoided.
- Patients at risk of ovarian hyperstimulation.