Artificial insemination: what is it and when does it need to be used?
Artificial insemination (AI) consists of depositing semen inside the female genitals. A woman’s partner’s semen can be used if he does not have any serious male fertility issues but, nowadays, inseminations are mainly carried out using semen from a sperm bank.
Índice
What does artificial insemination entail?
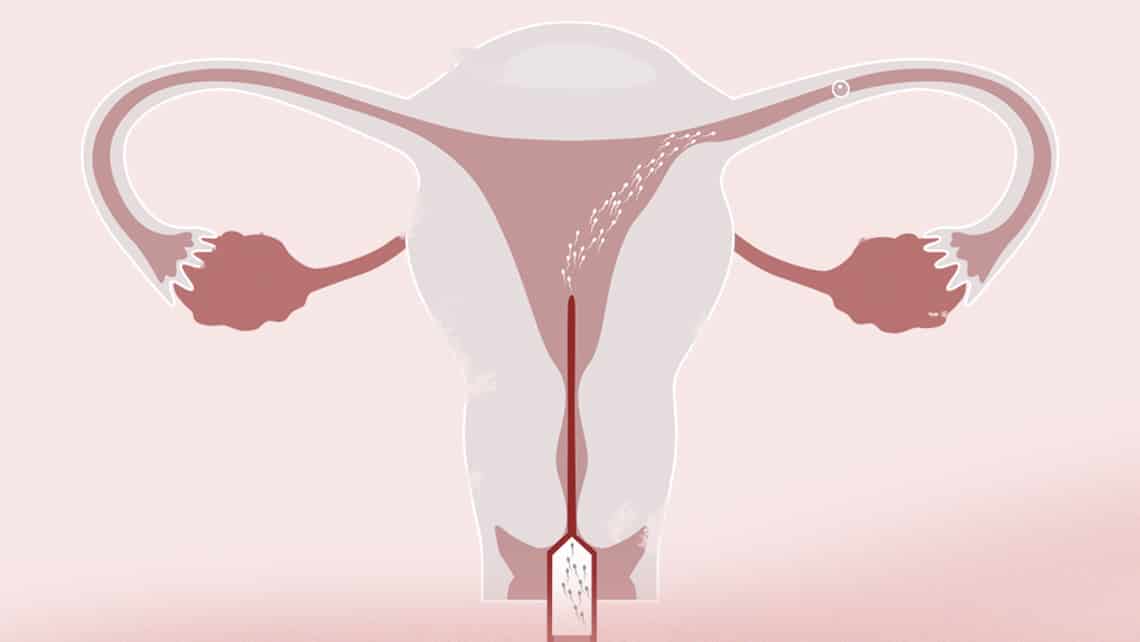
Insemination requires a strict control of when ovulation takes place. It is important to keep in mind that women only have a short period of very healthy fertility during the menstrual cycle and that the procedure needs to be carried out specifically on those days. In order to do so, either the cycle control is monitored or, more commonly, ovulation stimulation is performed. Two to three ultrasound checks need to be done in order to determine when is the best time to perform the procedure and so that the male partner can provide the sperm sample. Before being used, sperm needs to go through a process known as semen capacitation. Capacitation basically consists of selecting the spermatozoa with the greatest fertilising potential.
Once the sperm sample is ready, it is positioned inside the uterus using a very slim catheter that is really just a transportation system. The sample remains there until the oocyte that has just ovulated joins the strongest spermatozoa in the fallopian tubes and natural fertilisation takes place.
When does artificial insemination need to be used?
With artificial insemination, patients do not need an overnight stay in hospital and no changes to daily routine are necessary. It is an entirely outpatient procedure. On the whole, no more than 3 cycles are recommended because the likelihood of a pregnancy per cycle does not increase. This likelihood is rarely greater than 15% when the partner’s semen is used. However, results improve with sperm bank samples and this is mainly because the women assigned this treatment do not have fertility issues that affect the overall result.
Nowadays, it is estimated that around 20 to 25% of women under 35 years of age who undergo insemination at their request and without a male partner have a 20 to 25% chance of getting pregnant per course of treatment.
You can find more information about insemination on our website. LEARN MORE
Dr Rafael Bernabeu, Medical Director at Instituto Bernabeu.
